An evaporative condenser integrates air cooling and water evaporation to reject heat from refrigeration systems. Its design and operation differ fundamentally from standard air-cooled condensers:
1. Core Working Principle
Combined heat transfer:
Refrigerant heat dissipates through both:
Sensible heat transfer (air cooling coils)
Latent heat absorption (water evaporation)
Water spray system:
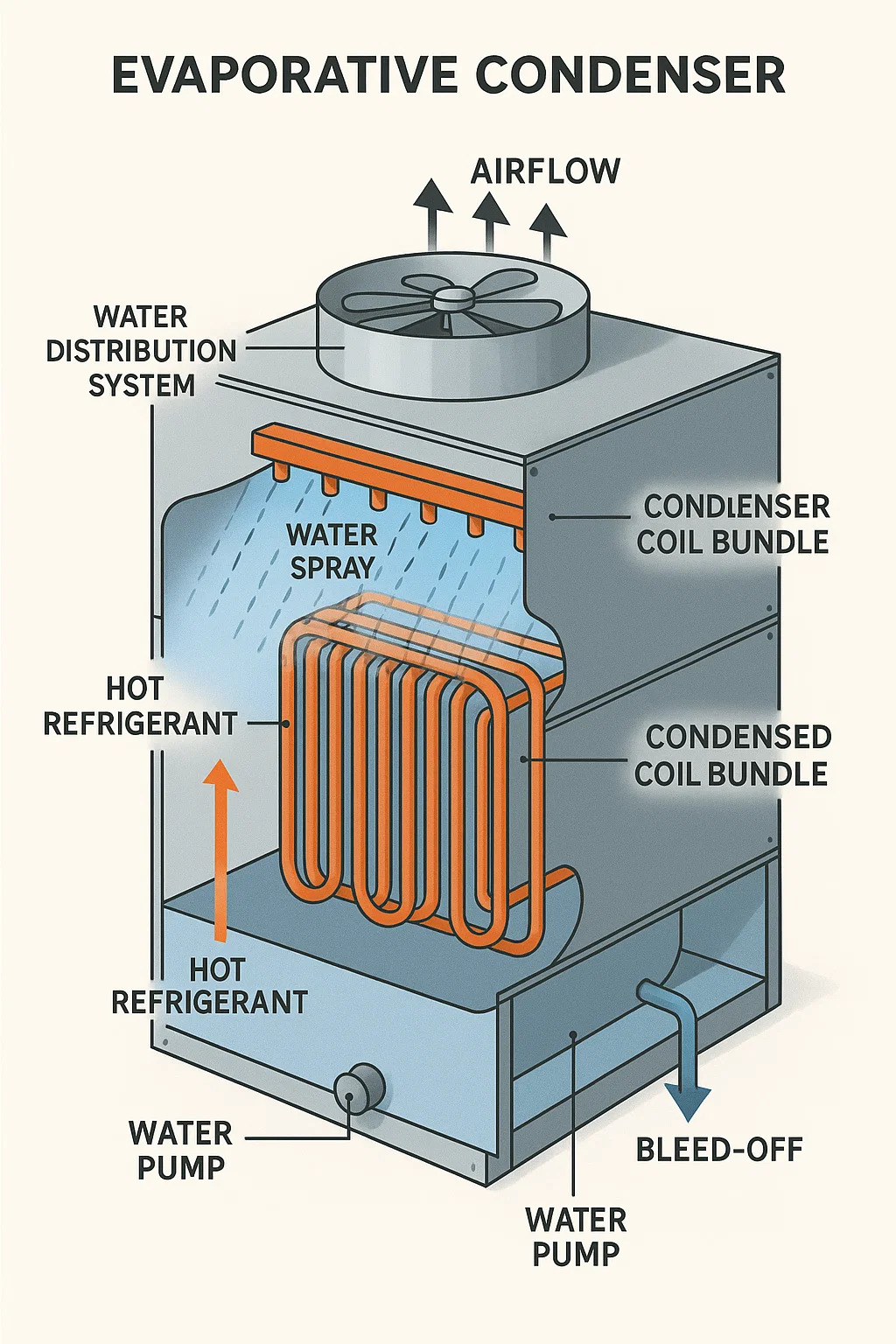
Pump circulates water over condenser coils.
Evaporating water absorbs significant heat, lowering refrigerant condensing temperature.
2. Critical Components
Condenser coil bundle:
Tubing circuit where hot refrigerant flows.
Typically copper or stainless steel for Typically copper or stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
Water distribution system:
Spray nozzles coat coils evenly; clogged nozzles cause dry spots and inefficiency.
Fans and airflow:
Forced-draft (fans atop unit) or induced-draft (fans below) configurations.
Air pulls through saturated coils, accelerating evaporation.
Sump and water treatment:
Collects and recirculates water.
Bleed-off valve controls mineral concentration.
3. Key Advantages
Superior efficiency in high ambient temps:
Water evaporation enables condensing temperatures below dry-bulb air temperature.
Reduced compressor workload:
Lower head pressure cuts energy use 20–30% vs. air-cooled units in arid climates.
Compact footprint:
Handles equivalent heat rejection with smaller coil surface vs. dry smaller coil surface vs. dry condensers.
4. Operational Constraints
Water quality demands:
Hard water causes mineral scaling; requires softeners/chemical treatment.
Poor treatment risks Legionella growth.
Freeze protection:
Winter operation demands glycol additives or drain-down in cold climates.
Drift and water loss:
Wind carries water droplets ("drift") – requires eliminator baffles.
Evaporation consumes water; unsustainable in drought regions.
5. Ideal Applications
Industrial refrigeration (cold storage, food processing).
High-ambient environments (desert climates).
Sites with abundant water but limited electrical capacity.
Maintenance Imperatives:
Scale removal: Acid washing coils annually. removal: Acid washing coils annually.
Drift eliminator cleaning: Prevents airflow blockage.
Bioprotocols: Quarterly Legionella testing for water systems.


 English
English عربى
عربى






